Preventing Workplace Violence in Healthcare with VR
Project Description
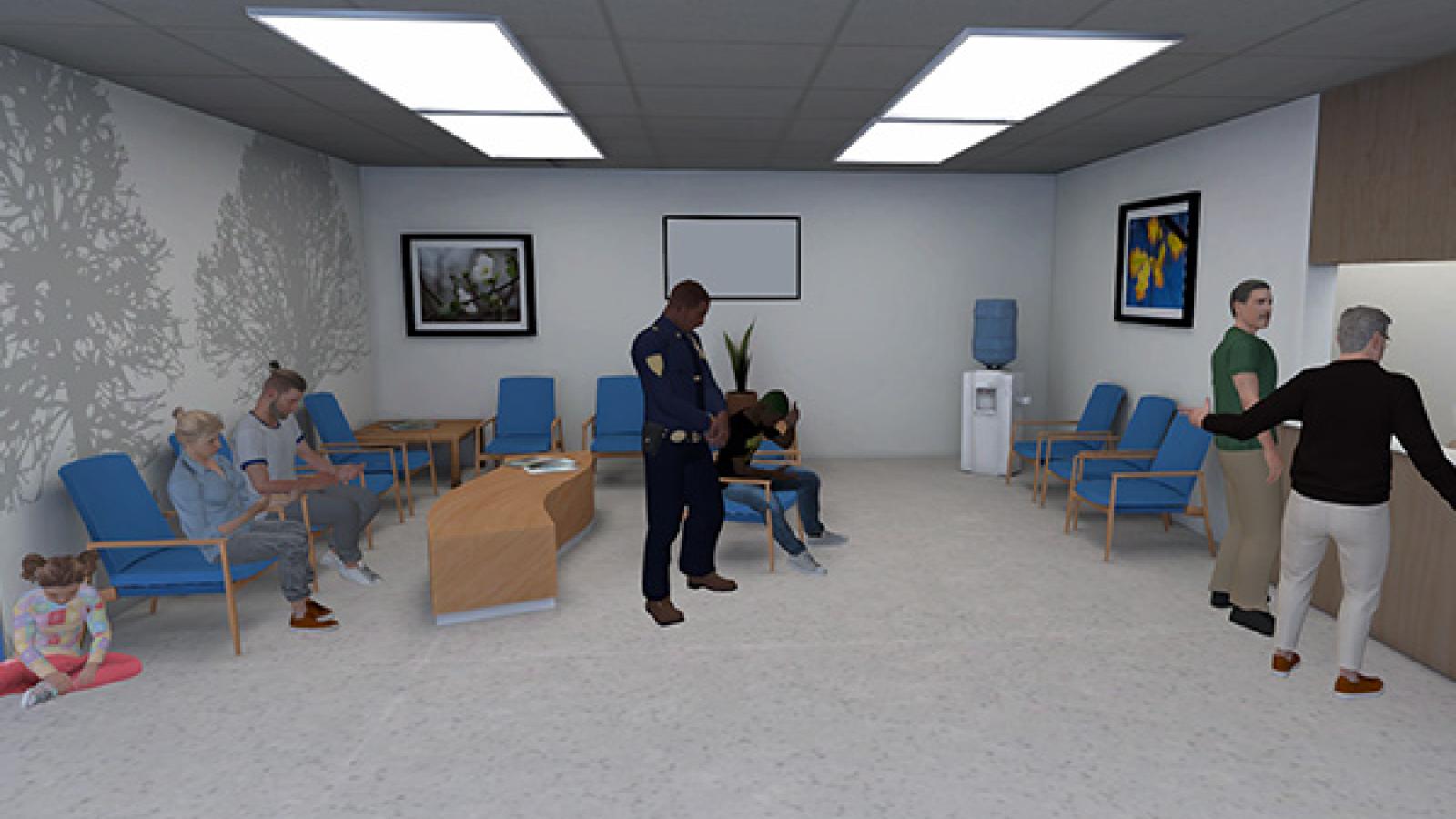
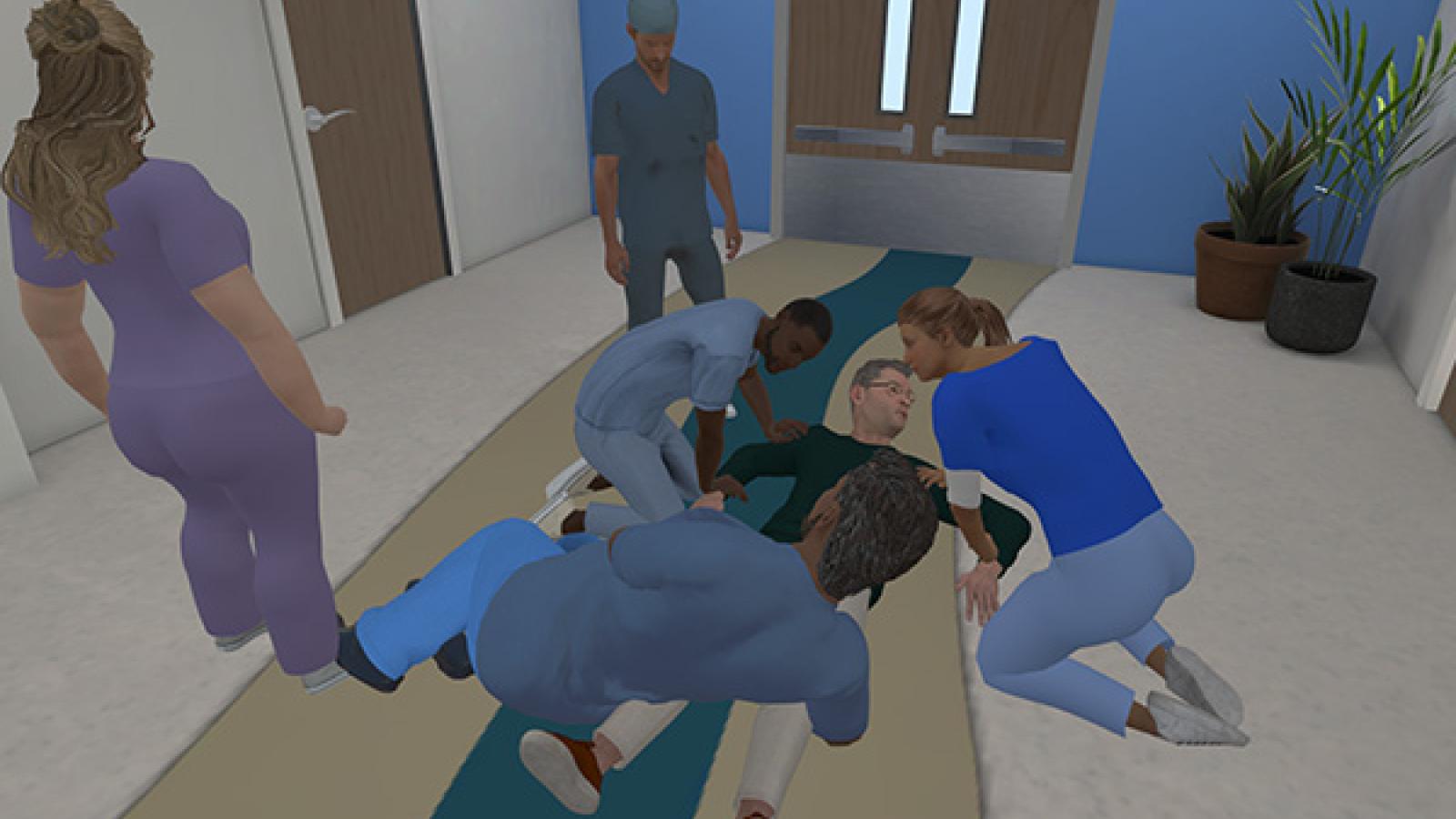
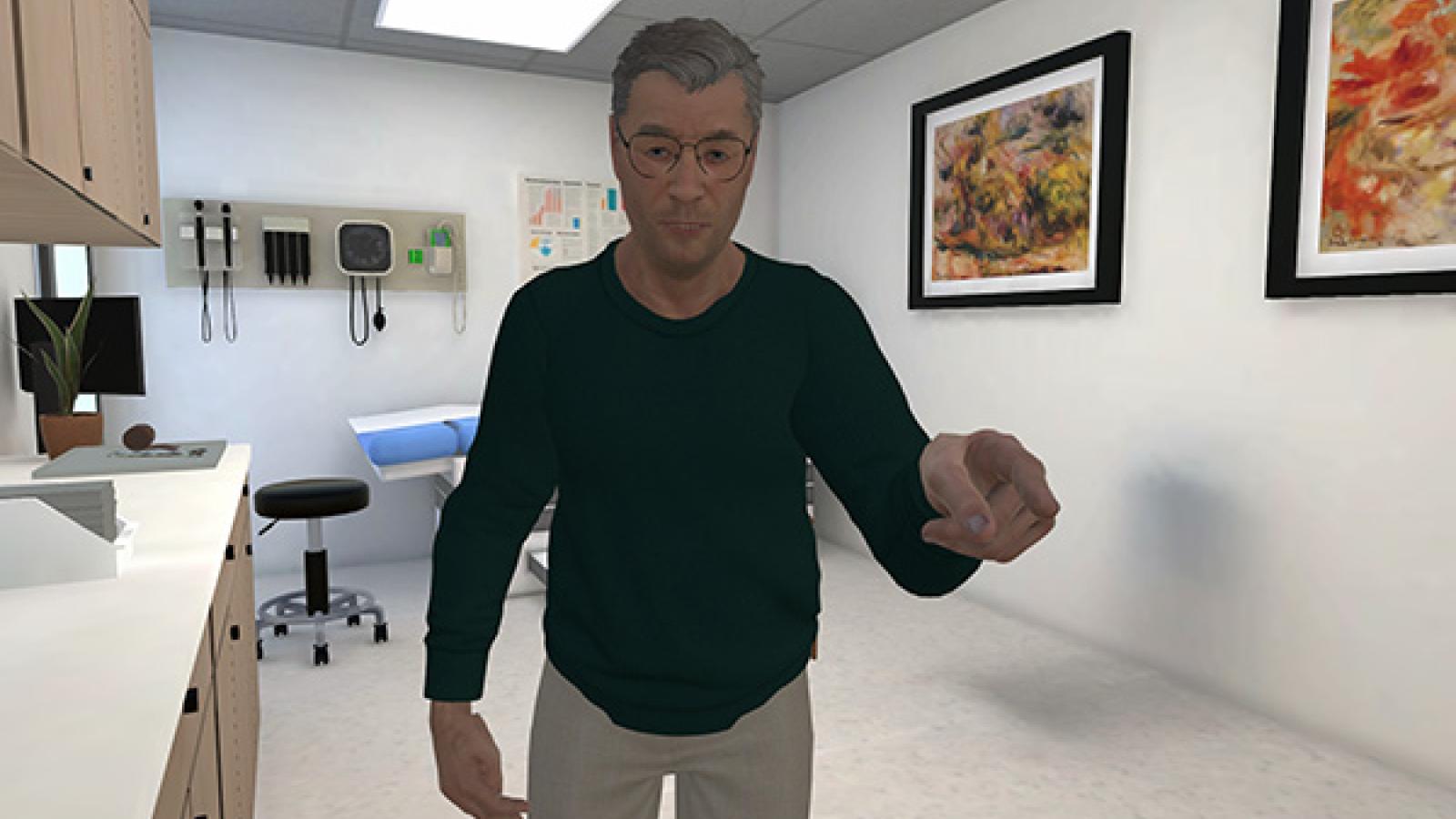
Nationwide Childrens’ Hospital has collaborated with ACCAD on performance capture for its virtual reality training simulation. It focuses on de-escalation of conflict between medical personnel and patients. The VR simulation features role-playing scenarios that feature interaction between patients, medical personnel and the hospital behavioral team.
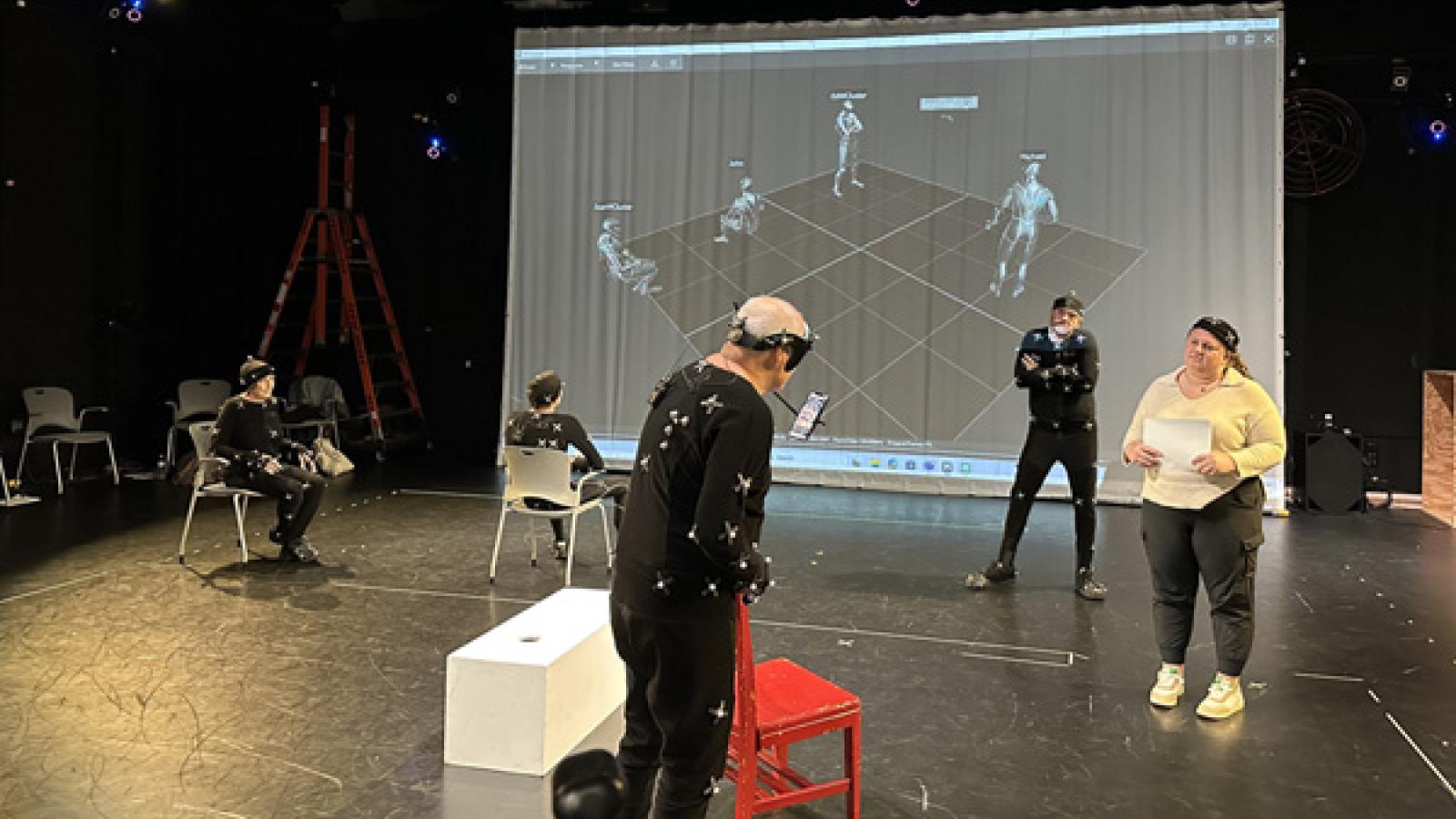
Performance capture was done for scenarios involving up to four actors. Facial capture of a leading performer in several scenarios and voice recording for all were also facilitated.
In addition to performance capture, the project offered a context and a test bed for ACCAD researchers to investigate aspects of related technologies that can benefit the current project as well as future related work.
Project Leads
- John Luna, Nationwide Childrens’ Hospital (Dance MFA 2018, ACCAD alum)
- Shadrick Addy, Assistant Professor, Department of Design/ACCAD
Key Personnel
- Vita Berezina-Blackburn, Sr Creative Technologist
- Jeremy Patterson, Graphics Researcher
- Mirkamil Majid (Mirkamili) (GRA, PhD Candidate, Department of Computer Science and Engineering)
- William Yuan, (GRA, MFA candidate, Department of Design)
Adjacent Research Projects
Hybrid Method System: A Reference Design and Implementation to Replace the Appearance of a Live Actor with a Synthetic Avatar Using Real-Time Motion Tracking in Mixed-Reality and Virtual Reality Education
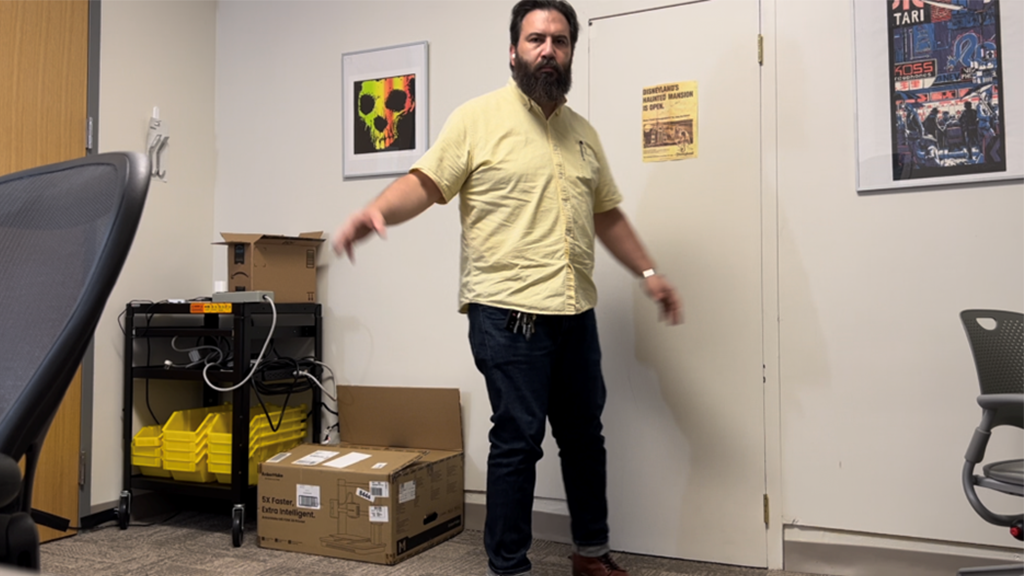
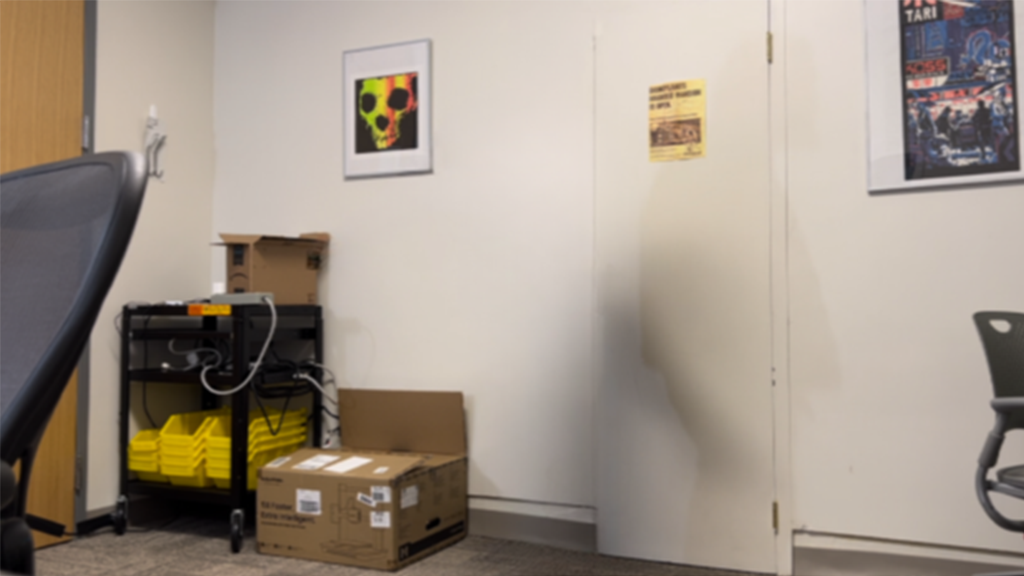
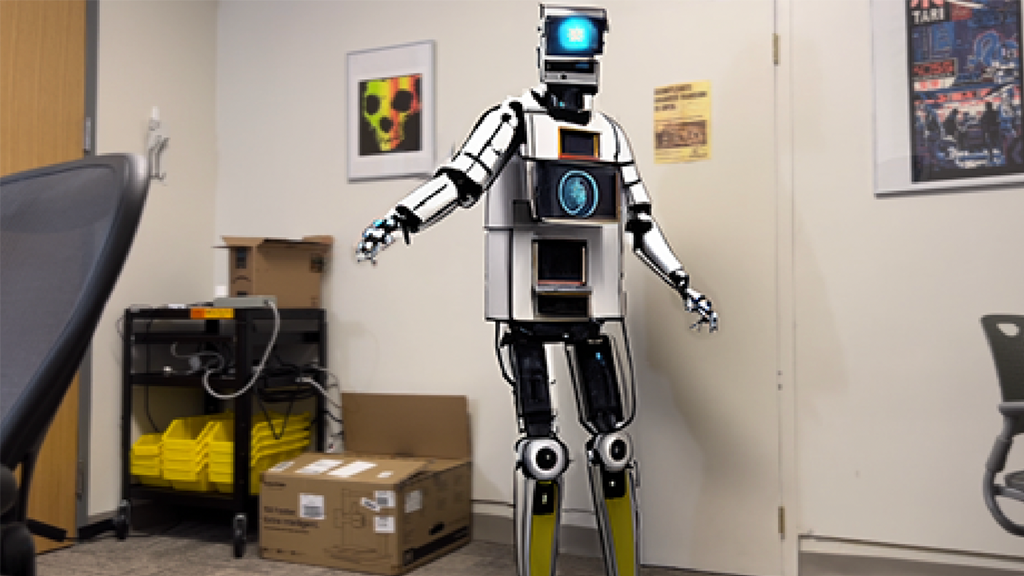
This prototype application hides the visibility of live actors while rendering synthetic avatars in their place using real-time motion tracking technology for training and education in mixed-reality (MR) and virtual reality (VR) settings.
In training and learning scenarios that rely on live role-play, this application will allow a physical actor to perform the part of a virtual avatar (i.e. medical patient) affording a wide gamut of possible avatar appearances and styles. At the same time, the learner views the actor through a capable head-mounted device (HMD) with mixed-reality capabilities. In real-time, the mixed-reality HMD will remove the appearance of the physical actor from view, replacing it with a character animated by the actor’s performance via real-time full-body pose capture. The proposed approach is aimed at implementation on Apple and Meta level devices but at the time of the project, in lieu of temporary hardware and software limitations, utilizes Apple iPhone. The implementation uses Apple VisionKit, CoreML, AVFoundation frameworks in conjunction with the LaMa open source AI model.



Motion Matching for NPC
In our endeavor to enhance multi-avatar training simulations, we developed a motion matching system prototype. Leveraging motion capture assets from ACCAD, we aimed to create realistic animations that improve the interaction between hospital workers and patients, incorporating behavior trees for more lifelike AI behavior.
Unlike the traditional game design methods that work with premade motion clips, motion matching technique dynamically selects the best animation frames from a large motion capture dataset in real-time, based on the character's current state and desired movement, resulting in more fluid and responsive animations. It adapts to dynamic environments and user input. By leveraging ACCAD’s motion capture facility, we harnessed real-world movement data to enhance our VR training simulations.
Prototype System
Our motion matching prototype system is set up in Unity and consists of the following components:
- Motion Database: We curated a diverse dataset of hospital-related movements, including interactions between medical staff, patients, and equipment. This database serves as the foundation for our animation synthesis.
- Matching Algorithm: Our custom algorithm is built on the foundation of Unity motion matching algorithm asset by Vault Break Studios. It leverages predefined scenarios, including hospital workers interacting with each other as they navigate the environment and responding empathetically to patients experiencing pain. It intelligently selects the most relevant motion clips from our database and seamlessly transitions between them, resulting in natural and lifelike animations.
- Behavior Trees: To enhance AI behavior, we integrated behavior trees into our system. These hierarchical structures govern decision-making for virtual characters, allowing them to respond realistically to user actions.
Future work will focus on expanding the animation database with diverse scenarios, refining AI behavior for complex interactions, other collaborative projects and opportunities for the evaluation and feedback.
Focus Tracking: Quantitative Approach to Estimate Focus of Attention of VR users Using Head Behavioral Data
Eye tracking technology gives accurate representation of focus but raises privacy and cost concerns. Focus tracking using head behavioral data may serve as a proxy which ensures better accessibility, privacy and safety. Shadrick Addy’s research aims to develop privacy-minded and cost-effective focus tracking methods using head behavioral data. Our goal is to provide accurate estimation of the focus of attention of VR users while ensuring accessibility, privacy and safety. Given head orientation, it would be possible to provide a probabilistic assessment of where a user’s focus of attention falls on a virtual object, ie the unit sphere. Further analysis will focus on developing Bayesian hierarchical models that incorporates factor effects, dependencies and individual differences. Longitudinal analyses will be necessary.